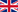
CFU: 9
Prerequisites
Basic knowledge of mechanics acquired in teaching Fundamentals of Mechanics; basic knowledge of the Matlab/Simunlink environment.
Preliminary Courses
Fondamenti di Meccanica
Learning Goals
Provide the student with the notions of some mechanical phenomena that can occur in the parts of the machines and the fundamental notions for the design of mechanical parts and the monitoring and diagnostic techniques during their operation. In addition, the basic elements of Robot Mechanics are covered.
Expected Learning Outcomes
Knowledge and understanding
The didactic activities included in the teaching aim to provide the student with all the methodological tools necessary to tackle the study of a mechanical system in general and of a robotic system in particular. The student must demonstrate knowledge and understanding of mechanical issues that are always present in any automatic or automated system. The lessons and exercises are aimed at developing in the student the causal links between the mechanical analysis and the functioning of the mechanisms also intended to constitute an automation system.
Applying knowledge and understanding
The course is aimed at transmitting the skills and methodological and operational tools necessary to concretely apply the knowledge relating to mechanical analysis in the monitoring and diagnostics of the mechanical systems themselves. The student will also have to demonstrate the ability to use the main synthesis phases of a robotic system, recognizing its main characteristics and kinematic structure, and demonstrating to be able to structure a kinematic and dynamic analysis of the system itself.
Course Content - Syllabus
- Stiffness and deformability of mechanical components
- Determination of the stresses in the machine parts
- Systems with multiple degrees of freedom
- inertia matrices and stiffness matrices
- equations of motion
- natural frequencies
- elastic lines
- Dynamics of rigid rotors
- Elements of dynamics of elastic rotors
- Critical flexural velocities
- Balancing of rigid rotors and balancing machines
- Notes on the balancing of elastic rotors
- Study of the kinematic and dynamic behavior of mechanical systems by computer simulation.
- Elements of Tribology
- Contact between surfaces
- Surface topography
- Wear mechanisms
- Properties of lubricants
- Main lubrication mechanisms
- Bearings and their sizing
- Criteria for diagnostics of mechanical elements
- Wavelet transform and applications
- Multi-solution analysis
- Chaos theory
- Mechanical system design example
- Industrial robots
- Definitions, general concepts
- Robots classification.
- Description and principles of operation of a robot.
- Motion transmission systems
- Gearboxes
- Actuators
- Other mechanical components for automation.
- Flat articulated systems with 1 d.o.f.
- Articulated quadrilaterals: kinematic study
- Kinematic synthesis
- Static Balancing
- Dynamic Balancing
- Articulated systems with n axes
- Direct and inverse kinematic problem
- Rotational matrices
- Homogeneous coordinates
- Transformation matrices
- Link structure and joint parameters
- Representation of Denavit and Hartemberg
- Gripper position
- Velocity matrix
- Acceleration matrix
- Statics of the arm
- Kinematic calibration
- Laws of motion and trajectories
- Minimum actuation time
- Scaling of the laws of motion
- Planning of the laws of motion and of the trajectories of a robot
- Trajectory of the gripper of an n-axis robot
- Dynamics
- Equations of dynamic equilibrium of a manipulator with several degrees of freedom
- Matrices of actions
- Forces that act on links
- Dynamic equilibrium of segments.
- Notes on the dynamics of non-rigid manipulators
Readings/Bibliography
Textbook: Vincenzo Niola, Giuseppe Quaremba - “Elemeti di dinamica non lineare di sistemi meccanici per l’Ingegneria. Dalla Trasformata Wavelet alla Teoria del Chaos”.
Textbook: Vincenzo Niola, Giuseppe Quaremba - “Sistemi Vibrazionali Complessi. Teoria, Applicazioni e metodologie Innovative di analisi”.
Textbook: C. Rossi – “Lezioni di Meccanica dei Robot” - Edizioni ESA, ISBN9788895430188
Lecture notes available on the teachers' websites.
Teaching Method
The teaching activities will be organized as follows: a) lectures for about 80% of the total hours, b) practical exercise in the classroom based on software Matlab (https://www.mathworks.com/) for about 20% of the total hours.
Examination/Evaluation criteria
Exam type
The oral exam follows three tests, distributed temporally at the beginning, at the center and at the end of the course, aimed at ascertaining the acquisition of the concepts and contents introduced during the lessons up to the moment of the test itself. Typically the student has 2 hours available for the exam which consists of answering 3 questions or numerical exercises. The three tests have equal weight on the final judgment.
Evaluation pattern
The outcome of the tests together with the outcome of the oral test allows you to formulate the judgment. Passing the tests alone is not sufficient to pass the exam. If the passed tests are not passed, the judgment is formulated only on the basis of the oral test.